Benefits of Automated Welding
What Is Automated Welding?
Today’s fabricators face growing expectations for higher product throughput on short timelines, coupled with the reality of the need to control or reduce overall costs. Automated welding is a highly efficient set of processes that can help fabricators meet these demands. Automated welding processes include the use of robotic and computer-controlled equipment and systems to create welds.
Table of Contents:Benefits of Welding Automation Help Increase Capacity and Throughput |
The most recognizable piece of equipment used in automated welding is a robotic arm, which holds the welding gun and performs the welds according to predetermined data points and instructions. Key components can include a welding power source and welding torch, a wire feed system, and a robotic arm with a controller. These are usually contained within a robotic welding cell with openings to load and unload parts to be welded.
However, welding automation isn’t only about robots. Hard (fixed) automation is an additional mode of automated welding. Hard automation generally focuses on heavy, repeatable welding on large pieces like pipes and vessels. When in use, equipment
for positioning is usually involved, manipulating or turning the piece that is being welded. The welding gun or torch is typically in a fixed position to help ensure consistency and repeatable welds.
Benefits of Welding Automation
Automated welding offers significant benefits to fabricators, making it a valuable tool for modern welding and manufacturing applications. Automated welding can help to:
→ boost productivity
→ increase capacity and throughput
→ protect and enhance weld quality
→ reduce cost per part
→ lower labor costs
Automated Welding Can Help Boost Productivity
Automating your welding allows for more precise and controlled processes, which helps with achieving consistent and repeatable weld quality by eliminating human variations in the weld process. 
Automated welding allows for:
→ Faster wire feed speeds resulting in higher deposition rates
→ Increased welding travel speeds
→ Less post weld cleanup
According to thefabricator.com, automated welding can produce parts 2.5 times faster than their human counterparts doing the same work, opening up time for
your welders to work on more difficult parts that are not suited to automation
In addition to high-quality welds, robots and automation equipment do not get tired or require rest. This means automated welding can help significantly
reduce downtime by avoiding post-weld processes and breaks needed by human welders.
Automated Welding can Help Increase Capacity and Throughput
Automated welding can significantly increase facility capacity. Along with boosting productivity during normal hours, automated systems and processes can run multiple shifts, empowering businesses to maximize their equipment and productivity. Automated welding is faster than manual welding and the additional time available to weld more parts can help increase capacity. More arc-on time can equate to more productivity, more pieces being welded in a shift, and greater throughput in the same shift. Automated welding can greatly help fabricators deliver more products to customers, helping them be more competitive.
Automated Welding Can Help Maintain Quality
Facilities work to hire welders appropriate for the job at hand. Welding skills demonstrated by experienced welders are extremely valuable. Hiring new welders could require a lot of time and resources. However, even skilled welders are not perfect. No two welders can reproduce the exact same weld. The human element always introduces variances and variables. Overlooked things such as the height and reach of individuals can change how they approach a weld before skills are brought to bear.
Unlike their human counterparts, welding robotics hold the torch at the same angle, maintain the same arc length and stick-out, start at the same beginning point, and maintain weld geometry throughout the weld, keeping these things within a minute
variance from weld to weld. This repeatability greatly reduces variations from weld to weld, which can result in more consistent deliverables and high-quality products. 
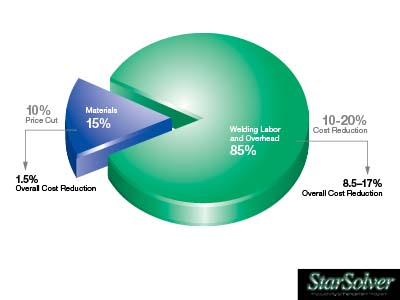
Automated Welding Can Help Improve Cost Efficiency
Some of the variances present with human welders can result in mistakes that may require repairs. To make such repairs, the weld may need to be cut and gouged out, followed by additional pre-weld prep and then rewelding the piece. In other welding operations, human variables can result in overwelding. Over-welding occurs when the movement during welding deposits filler metal in an area wider than what is necessary. When this happens, more welding wire is being used and deposited on the welded piece.
While on a single piece, the time spent with repairs and rewelding or the wasted material due to over-welding may not be a big concern. However, when repeated throughout a day’s shifts, it can lead to reduced cost efficiency as well as greater labor costs.
Automated welding provides greater control over weld settings and can repeat the same weld, again and again. The avoidance of weld repairs and over-welding can help to improve cost efficiency with less material waste and less downtime.
Automated Welding Can Help Lower Labor Costs
Some workers may feel threatened by the use of automated welding. However, these processes still need human oversight by qualified welders or workers. The concern can conversely become an advantage as it can enable a worker to get two to three times as much work accomplished. With the tooling and fixtures properly set for the welding process and products, setting them up from piece to piece can be simplified while at the same time helping to protect repeatability. This, along with the programmability, consistency, and repeatability of welds, as well as the reduced post-weld processing required, can help reduce overall labor costs.
Automated Welding Can Help Improve Your Competitive Advantages
Automated processes can give companies an edge by helping them create consistent and quality products at a lower cost due to less time and material waste. By protecting product quality while concurrently increasing productivity and throughput, automated welding can provide a significant competitive advantage. Improved efficiencies provide savings that impact fabricators’ bottom line. This can directly allow them to invest in more process improvements and automation, growing their business and capabilities.
Some may believe that automated welding and its benefits can only be enjoyed by larger businesses. However, whether you are a low volume / high mix shop or a high volume / low mix shop, Linde and many other manufacturers or distributors are helping
to break down barriers for smaller businesses, meaning they too will be able to implement automated welding to their own advantage.
Find Automated Welding Solutions
Linde’s PROSTAR™ LANCER™ Collaborative Robot (COBOT) is one example of how small to medium businesses can implement welding automation today. Designed for low-volume, high-mix work streams, Linde’s COBOT is an affordable and easy-to-program robotic welding platform with a 60 in. x 48 in. workspace, large enough for a variety of smaller, repeatable parts.
Linde’s automated welding specialists, our MetFab Productivity Specialists (MPS), are dedicated to helping customers improve productivity through process and facility audits using our STARSOLVER® Productivity Enhancement Program. Visit www.lindedirect.com/solutions/welding-automation-solutions to learn more about some of the automated welding products available and connect with your Linde representative to see how you can take advantage of automated welding.





























