What is a HeliStar Blend?
HeliStar™ Blends Argon, Helium, Argon/Helium and Argon/Hydrogen
Argon, helium, argon/helium and argon/hydrogen blends are used for a variety of TIG (gas tungsten arc) welding applications. Base material type and thickness, and the desired welding speed influence gas selection. A primary function of the shielding gas is to protect the tungsten electrode from oxidation. The DCEN or DCSP (electrode is negative polarity) power connection is used for carbon steel welding; AC with high frequency is recommended for aluminum.
Argon is recommended for manual welding of all materials. Its easy arc starting characteristics allow excellent control of arc voltage even as arc length varies with manual operations.
Helium is used to join thick plate and metals that rapidly conduct heat, such as aluminum and copper. Helium's high thermal conductivity creates a hotter, broader arc for higher welding speeds and deeper penetration. Arc starting and stability is not as good as argon. Increased gas flow rates and larger diameter electrodes must be used with helium shielding.
Linde's HeliStar™ argon/helium gas blends are used where increased heat input to the base material (helium) is desired while maintaining favorable arc starting and stability characteristics (argon).
Features
- Argon provides best arc stability/cleaning action
- Helium provides greater heat input
- Linde's HeliStar A-25, A-50 and A-75 offer balanced characteristics
Benefits
- First choice for TIG welding/good arc starting
- Maximum cleaning action (aluminum)
- Improved puddle fluidity and welding speed
- Better control of bead shape and distortion
- Good arc starting and increased heat input
- Deeper penetration as helium content increases
- Excellent bead shape and appearance
- Higher travel speeds on stainless steel; less distortion
- Excellent as a purge gas. Deeper penetration as helium content increases
Typical Applications
Argon
- Mild Steel
- Light Gauge Material
- Thin aluminum
Linde's HeliStar Blends
- Aluminum Ladders
- Aluminum Boats
- Copper Transformer Coils
Below are comparisons between shielding gas blends over a range of operating conditions. They are intended to provide suggestions for gas blend selection based on the criteria indicated.
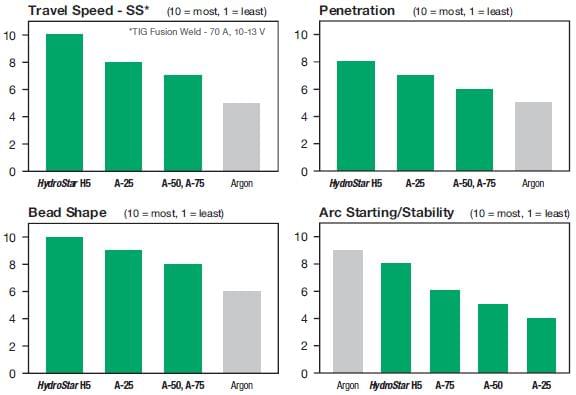
Note: The selection of the appropriate shielding gas can be complex due to the variety of operating variables (base metal chemistry and thickness, transfer type, wire selection and welding position). Consult your Linde representative to help you choose the best gas for your application.
Welding Conditions Table
| Wire Diameter (in) | Process | Tungsten Diameter | Current Level (amps) | Voltage (volts)* |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1/16 to 1/8 Carbon or Stainless Steel | GTAW | 1/16" diameter tungsten | 80-150 80-150 80-150 80-150 | 11-13 13-15 15-17 12-14 |
* Voltage level for 60 Hz power supply. Add 2-3 volts for 50 Hz models.




























